

Many local health departments manage reports of swimmer's itch by posting signs around bodies of water where people have contracted it. To prevent swimmer's itch, avoid swimming in warm, marshy waters where ducks and other waterfowl could be infected with the parasite. The more you swim in contaminated waters, the more intense and immediate the rash will be.
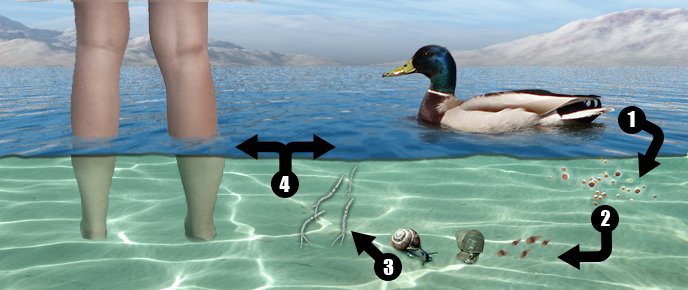
But with repeated exposures, the immune system learns to recognize and respond to the threat, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This parasite does not cause an infection, but it can be quite uncomfortable and bothersome. It generally happens in freshwater, but it can occasionally happen in salt water. The parasite doesn't affect humans in the long term, as the larvae die shortly after entering the body. Swimmer’s itch (cercarial dermatitis) is an itchy rash that can happen after swimming in natural bodies of water. An external file that holds a picture, illustration, etc.
Pictures of swimmers itch skin#
Other symptoms can include: itchy, red rash scaling or crusting small bumps or hives swollen or tender skin Your eyes may also be. If the parasite larvae gets under your skin, it can cause an itchy but otherwise benign rash. Swimmers itch may occur due to skin penetration by schistosome cercariae, while free-floating. Chlorine rash can cause the skin to itch after swimming. It often indicates a user profile.Ĭases of swimmer's itch occur every year, usually in early summer when the water is warmest. The rash, which can appear as small red bumps on the skin, is caused by microscopic parasites that reproduce in lakes, ponds, and oceans. The condition is a rash brought on by the body's allergic reaction to the larvae of certain microscopic parasites. It’s most common in freshwater lakes and ponds, but can occur in saltwater. Account icon An icon in the shape of a person's head and shoulders. Swimmer's itch (cercarial dermatitis) is an irritating rash that can develop after swimming or wading outdoors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
